Why is Color Important in Art?
Color is more than just a visual element in art; it’s a powerful language that speaks volumes. It can:
- Evoke emotions: Different colors are associated with various feelings, like red for excitement, blue for calmness, and green for growth. Artists use color strategically to evoke specific emotions in viewers.
- Set the mood: The overall color palette of an artwork can establish a specific mood or atmosphere. A painting dominated by cool blues might feel serene, while one filled with warm yellows and oranges might evoke a sense of joy.
- Symbolize meaning: Colors can hold symbolic meanings across cultures and historical periods. Gold might represent wealth or royalty, while white could symbolize purity or peace. Artists can leverage these symbolic associations to add depth and meaning to their work.
- Draw attention and create focus: Certain colors naturally capture our attention. Artists can use contrasting or complementary colors to draw the viewer’s eye to specific areas of the artwork, guiding their visual journey.
Historical Context of Color in Art
From the vibrant frescoes of the Renaissance to the bold abstractions of the 20th century, color has been a constant protagonist in the narrative of art history. Ancient civilizations utilized natural pigments to adorn cave walls and ceremonial objects, while the Renaissance masters pioneered techniques for capturing light and shadow with unprecedented realism. In the modern era, artists like Vincent van Gogh and Wassily Kandinsky pushed the boundaries of color usage, exploring its potential for conveying inner emotions and spiritual truths. Also, read about What are the 3 main types of art
Psychological Impact of Color
Research in psychology has underscored the profound effect that color can have on human emotions and behavior. Warm hues like red and orange are often associated with energy, passion, and excitement, while cool tones like blue and green evoke feelings of calmness, tranquility, and harmony. Understanding these psychological associations allows artists to strategically manipulate color to elicit specific responses from their audience, whether it be awe, nostalgia, or introspection.
Symbolism and Cultural Significance
Beyond its psychological impact, color also carries rich symbolic meanings that vary across different cultures and contexts. In Western cultures, for example, white is often associated with purity and innocence, whereas in many Asian cultures, it symbolizes mourning and death. Similarly, red may signify good fortune and prosperity in one culture, while symbolizing danger or aggression in another. By incorporating culturally relevant colors into their work, artists can imbue their creations with layers of meaning that resonate deeply with viewers from diverse backgrounds. Discover more about What is pattern in art
Color Theory and Techniques
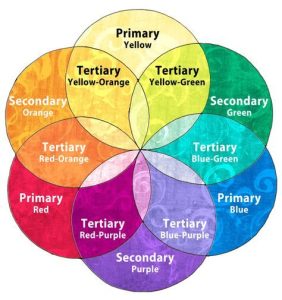
At the heart of effective color usage lies a solid understanding of color theory principles and techniques. The color wheel, comprised of primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, serves as a foundational tool for artists seeking to create harmonious color schemes and achieve desired visual effects. Techniques such as color mixing, shading, and contrast further enhance an artist’s ability to manipulate color to their advantage, allowing for greater depth, dimension, and realism in their compositions.
Expressive Power of Color
One of the most compelling aspects of color in art is its ability to evoke mood, atmosphere, and narrative without the need for explicit representation. A single stroke of crimson can convey the fiery intensity of a sunset, while a spectrum of blues and greens can transport the viewer to a tranquil seascape. Artists like Mark Rothko and Claude Monet are celebrated for their mastery of color, using bold, gestural strokes to evoke profound emotional responses and invite viewers into immersive sensory experiences.
Color in Different Art Forms
While color is often synonymous with painting, its influence extends far beyond the canvas. Sculptors harness the interplay of light and shadow to accentuate form and texture, while photographers manipulate color temperature and saturation to evoke mood and ambiance. In digital art, advancements in technology have opened up new possibilities for experimenting with color in virtual environments, blurring the boundaries between traditional and digital media.

Contemporary Trends in Color Usage
In the ever-evolving landscape of contemporary art, artists continue to push the boundaries of color usage in innovative and unexpected ways. From the vibrant palettes of street artists to the subdued minimalism of conceptual art, there is a wide spectrum of approaches to color that reflect the diversity of artistic expression in the 21st century. Emerging artists like Olafur Eliasson and Yayoi Kusama are renowned for their immersive installations that captivate audiences with their bold use of color and form. Read more about What is shape in art
Practical Applications of Color in Art
For aspiring artists looking to harness the power of color in their work, there are a myriad of resources and techniques available to explore. Experimenting with different color palettes, studying the works of master artists, and seeking feedback from peers can all contribute to a deeper understanding of color theory and its practical applications. By embracing the limitless possibilities of color, artists can unlock new dimensions of creativity and expression in their artistic practice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, color serves as a universal language in the world of art, transcending cultural and linguistic barriers to communication on a deeply visceral level. Whether used to evoke emotion, convey symbolism, or simply delight the senses, color plays an indispensable role in shaping our perception of the world around us. By understanding the principles of color theory and embracing the expressive potential of color, artists can enrich their creative practice and connect with audiences in meaningful and profound ways.
FAQs
What role does color play in abstract art?
Abstract artists often use color as the primary means of expression, relying on vibrant hues and bold compositions to convey emotion and energy.
How does cultural background influence color preferences in art?
Cultural norms and traditions heavily influence our perception of color, shaping our preferences and associations with certain hues and tones.
Can color be used to evoke specific emotions universally?
While certain colors may have universal associations with emotions, the interpretation of color can also be highly subjective and culturally contingent.
Are there any famous artists known for their unique approach to color?
Artists like Henri Matisse and Georgia O’Keeffe are celebrated for their innovative use of color, pushing the boundaries of traditional color theory in their respective styles.
How can artists overcome creative blocks related to color choices?
Experimentation, observation, and seeking inspiration from nature and other art forms can help artists overcome creative blocks and discover new approaches to color in their work.